
Removing code safely and securely is often easier said than done. A powerful integration between Azul Intelligence Cloud and OpenRewrite enables enterprises to automatically identify, flag, and remove unused and dead code safely and securely.
In this post you will learn:
- OpenRewrite is an open-source auto-refactoring engine with recipes that can be used to execute large-scale code changes safely
- The integration between Azul Code Inventory and Open Rewrite enables enterprises to automatically identify, flag, and remove unused and dead code
- An incremental process enables enterprises to check code safety at every step
Code that runs as part of outdated tests but never in production is often referred to as unused or dead code. As long as it doesn’t run, it doesn’t hurt anything, but it becomes clutter that interrupts teams as they try to work on active code. It increases maintenance effort and slows development velocity.
Studies show that people take an average of 23 minutes to resume full focus after an interruption, so it's no surprise that keeping unused code around is problematic. Knowing which code to remove is one thing. Unfortunately, removing code safely and securely is often easier said than done because it's difficult to automate. To get around this problem, Azul has created an OpenRewrite plugin to help automate and accelerate Java application modernization efforts by streamlining the removal of unused and dead code.
Automatically remove technical debt
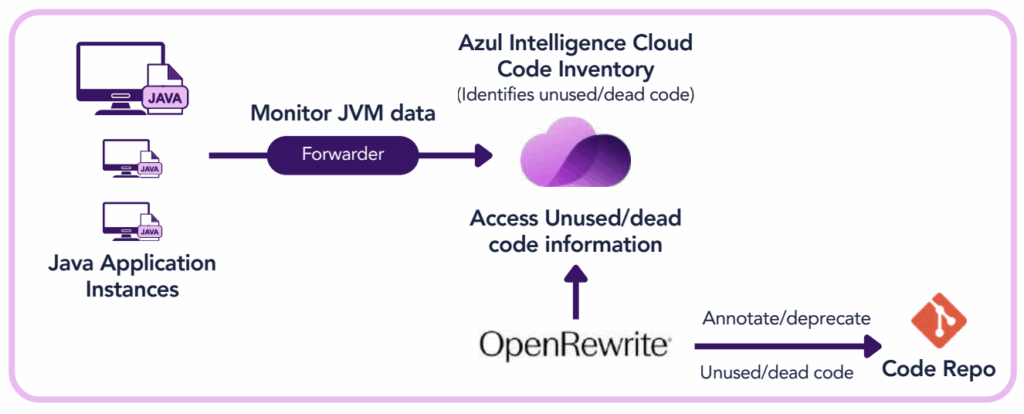
OpenRewrite is an open-source auto-refactoring engine whose recipes can be used as tools that work through large-scale code changes and execute them safely across multiple repositories. By combining Azul Code Inventory’s deep runtime visibility and Java expertise with OpenRewrite’s powerful engine for automated, multi-repository, rules-based code refactoring, enterprises can automatically identify, flag, and subsequently remove unused and dead code safely and securely.
Step-by-Step Process
Making changes to application codebases is a high-stakes endeavor, and enterprises are right to be nervous about third-party solutions implementing automatic changes.
This is why Azul’s OpenRewrite plugin puts updates through incremental steps over time before executing changes, while keeping developers aware through code annotations. Enterprises are always in control and can set the timing for each phase of the process. A sample process might look like this:
- Step 1: Azul Code Inventory monitors JVMs and collects key information on which code is and is not being used.
- Step 2: Based on this information, OpenRewrite annotates the codebase to indicate which sections will (eventually) be deprecated. At any point, if Code Inventory finds that code marked for deprecation actually does get run, the plugin will automatically remove the annotation.
- Step 3: When teams are ready, the plugin can automatically mark code as approved for removal
- Step 4: Development teams can now remove references to the deprecated classes on their schedule. This step surfaces unit tests associated with unused and dead code since these tests will break.
- Step 5: Once the teams have full confidence that the code can be safely removed, the unused/dead code can be removed.
Find out more
Azul and OpenRewrite give development teams an accurate and automated way to remove unused and dead code from their applications, which is a critical step to ensure application modernization success. As a result, enterprises can dramatically reduce the time, resources and costs associated with identifying and removing technical debt.
By combining Azul’s production-aware insights with OpenRewrite’s ability to safely and automatically transform code at scale, enterprises have a clear path to avoiding the looming “End of Support” crunch for their entire Java estate. It also provides a model for how runtime data and automated codebase updates can work together going forward to keep codebases lean, secure and ready for what’s next.
The quickest way to get started may be to engage with one of Azul’s partners that offer Java app modernization services. Partners are trained and certified by Azul, and can deliver strategic advice that can help minimize risk while project-managing your modernization projects at the kind of scale necessary to avoid the pending end of support crisis
To learn more about how Azul Intelligence Cloud works, read our new ebook, The Java Application Modernization Crisis.





