What is a Cloud Strategy?
A cloud strategy is a set of detailed steps that outline how an organization can leverage cloud technology to accomplish its primary business objectives. The strategy is just as important as the adoption process on the IT road map.
A solid strategy ensures that all implemented cloud solutions are deployed systematically, efficiently, and securely. Also, a well-defined strategy enables businesses to capitalize on the systems and solutions they already have when switching to the cloud.
What are the benefits of cloud strategy?
A suitable cloud strategy can bring numerous advantages to an organization looking into cloud adoption, such as:
- Cost and resource optimization: Cloud services often operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to minimize their upfront investments, purchasing only the hardware and software resources and expertise they need for their cloud project.
- Designing for flexibility and scalability: Organizations can create a cloud infrastructure with scalability and flexibility in mind, letting them adapt to changing market conditions and consumer demands.
- Improving business agility and innovation: Leveraging the latest cloud technologies can help companies quickly and effectively develop and deploy new apps, services, and features. This allows them to maintain a competitive edge.
- Enhanced data security and compliance: Third-party providers of cloud services often invest heavily in security measures to comply with high regulatory standards. Businesses can benefit greatly from these security advancements by working with a suitable cloud provider.
- Increased collaboration and accessibility: Well-planned cloud solutions allow employees to readily access data, applications, and systems from anywhere, fostering a culture of collaboration and enhancing overall productivity.
What does a cloud strategy architecture look like?
The architecture of a cloud strategy encompasses several essential components that create a cohesive, efficient, and secure cloud environment:
- Cloud deployment model: An organization can choose between public, private, and hybrid clouds. A public cloud deployment model, also known as a multi-cloud strategy, is the cheapest but utilizes resource sharing. A private cloud is the opposite, allocating an entire cloud server to a single organization. A hybrid cloud-first strategy combines the public and private cloud models.
- Cloud service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the primary cloud service models, with varying degrees of control, customization, and responsibility allocated to the business.
- Cloud management and orchestration tools: Specialized tools facilitate the monitoring, managing, and optimizing of cloud resources. They ensure efficient and seamless operations across the entirety of the cloud ecosystem.
- Legacy system integration: A successful cloud strategy must consider infrastructure and legacy systems that they may be able to integrate with the cloud environment. It enables organizations to proceed with existing business operations, reducing the time needed to train staff on new apps.
- Security and compliance measures: Businesses must also ensure their cloud adoption strategy adheres to industry-specific regulations, incorporating cutting-edge security measures to protect user and business data.
What is the purpose of a cloud strategy?
The primary purpose of planning a cloud strategy is to align cloud adoption with business objectives, ensuring that organizations fully capitalize on the benefits of cloud technology. It’s an integral first step where businesses must thoroughly assess their current infrastructure and short- and long-term goals.
Furthermore, a reliable cloud strategy allows organizations to maximize their return on investment, ensuring they don’t waste time, money, and effort on implementing features they may not need later on. Planning is also necessary to seamlessly implement and integrate cloud technology. Otherwise, incompatibility problems may occur between cloud services, legacy systems, and applications.
How does a cloud strategy work?
A business’s cloud strategy is the plan for adopting a cloud architecture to harness the power of cloud computing. It’s a holistic approach to the digital transformation processes of integrating cloud-based solutions with legacy systems and applications.
It’s responsible for handling the adoption from multiple angles: economic, staff readiness, stakeholder approval, client feedback, and realistic timescales. Primarily, a successful cloud strategy fosters innovation that aligns with available and attainable IT resources, helping them work toward achieving business goals.
Another important part of the strategy is preparing for potential risks and challenges. This enables organizations to navigate the complexities and lack of predictability of cloud adoption, mitigating damages and staying on the right path. Ultimately, cloud strategies are a vision and a road map that helps organizations leverage new technology while minimizing risks, optimizing growth opportunities, increasing productivity, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
How do enterprises adopt a cloud strategy?
When designing a cloud strategy, there are several key factors that an organization needs to consider:
- Assessing organizational readiness: Evaluating existing infrastructure, legacy systems, and processes to determine the best path forward for cloud implementation.
- Defining clear objectives: Establish measurable goals and benchmarks for the cloud implementation strategy, ensuring it aligns with the business objectives.
- Selecting suitable cloud models: Based on needs and objectives, businesses must choose between public, private, and hybrid cloud deployment strategies and select the right service model between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
- Preparing a cloud migration strategy: Create a detailed data and system migration plan that goes step-by-step into the timeline of moving to the cloud and implementing solutions of choice.
- Monitoring and optimization: Ongoing management and optimization are crucial for maintaining the peak performance of the cloud and ensuring its long-term success.
Who is responsible for cloud strategy?
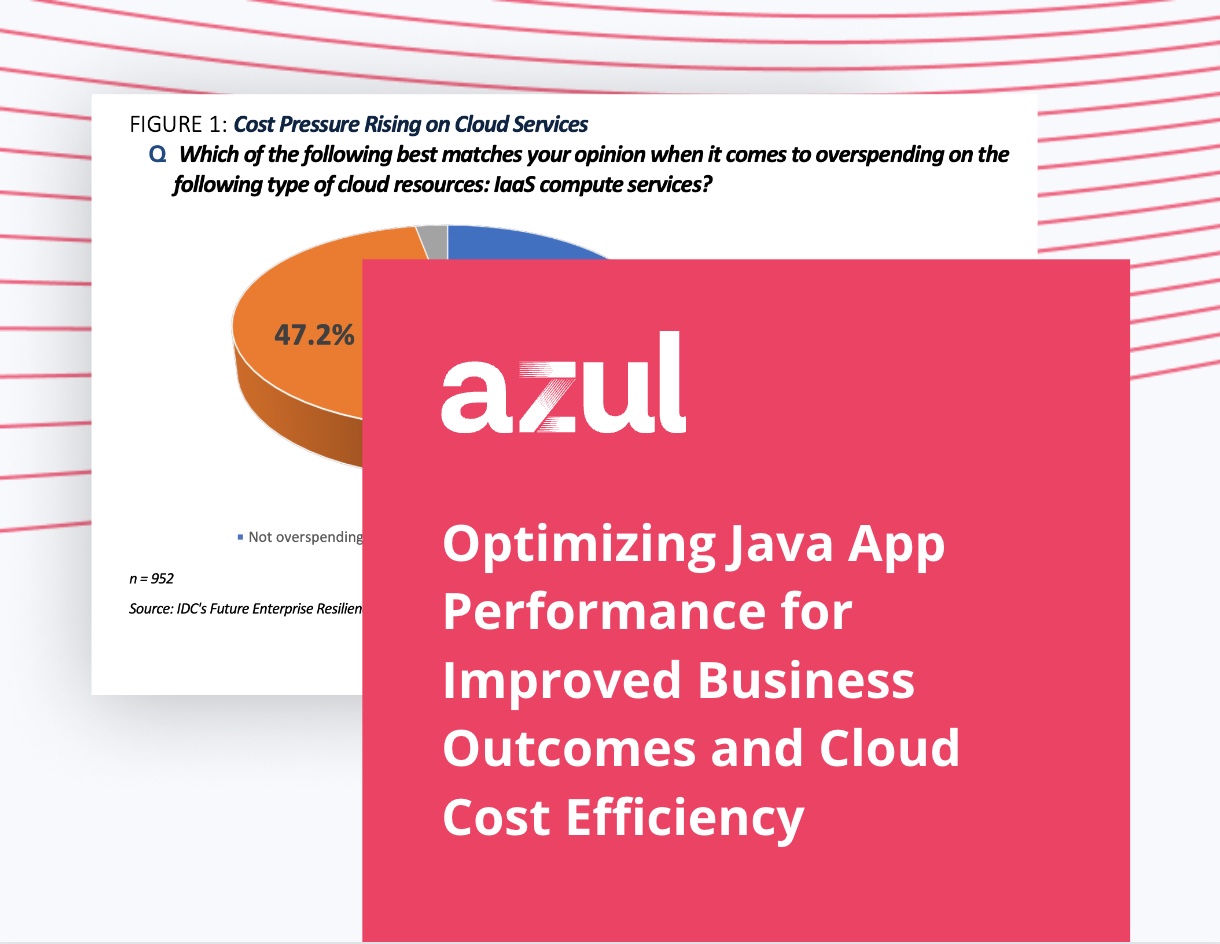
According to the Azul State of Java Survey and Report 2023, IT Ops is the number-one leader in cloud cost optimization (45%), followed by the CTO (36%), cloud architect (28%), and Cloud Center of Excellence (27%).
Formulating and executing a cloud strategy requires immense collaborative efforts involving C-level executives, IT leaders, and various departments within the organization and its branches. IT teams play a critical role in implementing and managing cloud solutions, but business-oriented departments are more adept at identifying specific needs and goals.
In some cases, organizations may need to engage external cloud consultants or managed service providers to assist them with developing and implementing their cloud strategy.
What risks are involved with cloud strategy?
Similarly to any other business endeavor, there are several risks associated with cloud technology adoption that organizations should brace for, such as:
- Data security and privacy concerns: Organizations are responsible for ensuring the security and safeguarding of sensitive customer and business data stored in the cloud.
- Regulatory compliance: Legal issues may arise if businesses don’t adhere to their industry’s regulations and legal requirements for data processing and storage. This may lead to hefty fines or legal action against them.
- Misaligned expectation: Failing to prepare for things to go wrong and manage their expectations accordingly may leave businesses dissatisfied with the results or the cloud adoption journey. This could discourage employees, investors, and stakeholders from future, often necessary, development endeavors.
- Miscalculating downtime: Downtime and service disruptions are normal in a cloud environment. However, failing to accurately calculate and prepare for downtime may result in disappointed customers and business partners.
How does Azul help with cloud strategy?
Azul Platform Prime improves efficiency and lowers the cost of running your internal development platform. It improves large-scale Kafka installations, giving you up to 45% more throughput and reducing overall latency. Prime delivers better price and performance for large Elastic/logstash, Splunk, or Promethius installations. With Prime, you can enhance your pre-built container images to make systems and applications go further with lower latency and higher throughput. Images are built using a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that makes production code start fast, go fast, and stay fast. You get the fastest machine code no matter what compute platform you are using.
A key element of FinOps framesworks is improving governance and cloud cost controls without sacrificing performance.
faster code = less compute consumed = lower cloud bill
Increase Apache Cassandra throughput and density while maintaining service levels.
Consider these critical questions when looking for using Java to reduce cloud waste:
- Are you over-provisioning to address business requirements?
- Are you running code slower than it can go?
- Does workload inconsistency mean you need to provision more headroom?
- Are sprawling infrastructure software technologies driving your costs higher?
- Are common services in your application and development platform not cost efficient?
- Is the cost to serve increasing faster than your business growth?
- Are you not using what you pay for efficiently?
Azul Platform Prime
A truly superior Java platform that can cut your infrastructure costs in half.